The Middle East: A $60 Billion Opportunity for Beauty Brands
The Middle East, often celebrated as the "cradle of civilization," is renowned for its rich history, vibrant culture, and enduring traditions. Among its many contributions to global society, the region's beauty rituals and skincare practices have stood out, refined over centuries and passed down through generations. Today, the Middle East's beauty industry is a thriving and rapidly expanding market, drawing attention from both local entrepreneurs and international brands eager to tap into its vast potential.
Understanding the Middle East
To fully appreciate the dynamics of the Middle Eastern beauty market, it's essential to define what constitutes the Middle East. Geographically, this region spans Southwest Asia and parts of North Africa, encompassing nations along the southern and eastern shores of the Mediterranean Sea, extending as far as Iran. According to Britannica, the Middle East includes countries such as Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Qatar, Kuwait, Oman, Bahrain, Jordan, Lebanon, Egypt, Turkey, and Iran, among others. These nations share historical, cultural, and religious ties, creating a cohesive yet diverse marketplace.
The Growing Beauty Market in the Middle East
The beauty and personal care sector in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region has experienced remarkable growth over the past decade. Currently valued at over $46 billion, projections indicate it will surpass $60 billion in the near future. Several key factors drive this expansion:
Economic Development : Many Middle Eastern countries have witnessed significant economic growth, leading to increased disposable incomes. This financial stability enables consumers to invest more in beauty and personal care products.
Urbanization : Rapid urbanization has exposed more individuals to global beauty trends and innovations, boosting demand for a wide array of beauty solutions.
Youthful Population : With an average consumer age of just 32, the Middle East boasts a young, tech-savvy demographic. For example, in the UAE, 60% of the population is under 25, while in Saudi Arabia, approximately 70% are under 30. This youthful audience is highly receptive to new products and heavily influenced by digital platforms like social media.
Consumer Spending Trends
Understanding how consumers allocate their budgets is critical for brands aiming to enter the Middle Eastern market. In the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries - Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE—there are notable differences in spending patterns between genders:
Women : On average, women dedicate $63 per month to makeup and $52 to skincare products.
Men : Men spend around $16 per month on skincare, reflecting a growing interest in grooming and self-care.
These figures underscore the substantial opportunities available for both women's and men's beauty products, with an increasing focus on male grooming.
Entering the Market: A Strategic Approach
For brands looking to establish themselves in the Middle East, adopting a country-specific strategy is crucial. While the UAE is often seen as the gateway due to its cosmopolitan appeal and advanced retail infrastructure, it's important to recognize that consumer preferences, purchasing power, and regulatory environments can differ significantly across the region.
Key Considerations for Market Entry
Customized Marketing Campaigns : Brands must tailor their marketing efforts to align with local tastes and values. Authenticity is vital; while adapting to regional preferences, maintaining the brand's unique identity ensures differentiation in a competitive landscape.
Collaborating with Local Partners : Partnering with local entities that possess deep market knowledge and experience is invaluable. These partners can navigate the complex retail ecosystem, provide insights into consumer behavior, and ensure compliance with local regulations. It's equally important that these collaborators respect the brand's DNA to preserve consistency and integrity.
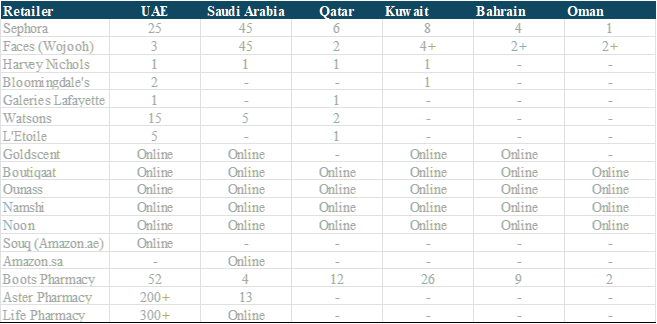
Navigating Distribution Channels : The Middle Eastern retail environment is fragmented, offering multiple avenues for product distribution:
Prestige Retailers : High-end establishments like Sephora and Faces offer premium beauty products and maintain a strong presence in major cities.
Department Stores : Luxury retailers such as Harvey Nichols and Bloomingdale's serve as platforms for high-end beauty brands.
FMCG Outlets : Pharmacies and supermarkets like Watsons and Spinneys cater to everyday beauty and personal care needs.
E-Commerce Platforms : Online shopping is gaining traction, with regional players like Ounass, Namshi, alongside global giants like Amazon, serving the market.
Spas and Salons : These venues not only provide services but also sell beauty products, offering brands access to consumers seeking professional-grade solutions.
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) : Brands are increasingly focusing on their own e-commerce platforms, branded stores, and pop-up events to engage directly with customers.
Local Chains/Stores: the local national beauty chains that have a massive weight on the market, like Paris Gallery, Laure, L'Odore in KSA, Vavavoom, Coop, Beidoun in Kuwait, Pari Gallery, Secret Notes in Qatar, Limited Gallery, Atelier Perfumery, Plethora, HOB in the UAE, Al Hawaj in Bahrain... all those can have up to around 30-35 stores and represent a significant part of what the beauty business is in the Middle East, in terms of business and brand image.
Case Study: Sephora's Success in the Middle East
Sephora, a French beauty retailer established in 1969, entered the Middle Eastern market in 2007. Since then, it has become a dominant force, known for its service-oriented approach and extensive product range. As of recent reports, Sephora operates approximately 66 stores across the region, including locations in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, and Bahrain. Its flagship store in Dubai Mall ranks as the company's top-performing location globally, highlighting the region's significance.
Sephora Middle East stocks a mix of international and local brands, reflecting the region's blend of tradition and modernity. For instance, Huda Beauty, founded by Dubai-based entrepreneur Huda Kattan, has emerged as one of the best-selling cosmetic brands in Sephora's Middle Eastern stores. This success demonstrates how local brands can thrive alongside global competitors by leveraging regional preferences and effective marketing strategies.
Embracing Digital Transformation
The digital landscape in the Middle East is evolving rapidly, with e-commerce playing an increasingly pivotal role in the beauty industry. Factors driving this shift include:
High Internet Penetration : Countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia boast some of the highest internet penetration rates worldwide, facilitating online shopping.
Mobile Commerce : A large portion of the population uses smartphones, making mobile commerce a critical channel for reaching consumers.
Social Media Influence : Platforms like Instagram, Snapchat, and TikTok are highly popular, with beauty influencers shaping consumer preferences and trends.
Brands entering the Middle Eastern market should prioritize a robust digital strategy, incorporating user-friendly e-commerce platforms, active social media engagement, and collaborations with local influencers to build brand awareness and trust.
Cultural Sensitivities and Regulatory Compliance
Respecting cultural nuances is paramount for success in the Middle East. Brands must ensure that their products, marketing materials, and overall messaging align with local values and norms. Key considerations include:
Modest Advertising : Marketing campaigns should adhere to cultural standards of modesty, avoiding content that may be deemed inappropriate.
Halal Certification : Obtaining Halal certification for skincare and cosmetics can be advantageous, as it assures consumers that the products comply with Islamic dietary laws.
Navigating the Regulatory Environment
Each country within the Middle East may have its own set of regulations, but there are overarching themes and standards that brands should be aware of to ensure compliance and successful market entry.
General Standards and Compliance
The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), comprising Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE, has established unified standards for cosmetic products to ensure consumer safety and product quality. One of the primary standards is GSO 1943/2016, which outlines general requirements for cosmetic products, including safety assessments, permissible ingredients, and labeling guidelines. Compliance with this standard is mandatory for products marketed within GCC countries.
Country-Specific Regulations
While there are unified standards, individual countries may impose additional requirements:
United Arab Emirates (UAE) : The UAE enforces strict regulations to ensure the safety and quality of cosmetic products. All products must undergo registration with the Ministry of Health and Prevention (MOHAP) before being marketed. This process involves a thorough review of product ingredients, safety assessments, and compliance with labeling standards.
Saudi Arabia : The Saudi Food and Drug Authority (SFDA) oversees the regulation of cosmetic products. Brands must register their products through the SFDA's electronic system, ensuring adherence to safety and labeling standards. Additionally, products must be free from prohibited substances and avoid misleading claims.
Labeling and Packaging Requirements
Accurate labeling is essential in the Middle Eastern beauty market. Labels must provide clear information about the product, including:
Product name
Ingredients list (in descending order of concentration)
Manufacturer details
Country of origin
Usage instructions
Expiration date
Labels must be bilingual, featuring both Arabic and English, to cater to the diverse consumer base and comply with local regulations.
Safety and Quality Assurance
Brands are required to conduct comprehensive safety assessments for their products. This includes stability testing to ensure product integrity under various conditions and microbiological testing to confirm the absence of harmful microorganisms. Maintaining detailed records of these assessments is crucial, as regulatory authorities may request documentation to verify compliance.
Retailer and Distributor Compliance
Retailers and distributors play a vital role in ensuring compliance. They must verify that the products they stock have undergone necessary registration and meet all regulatory standards. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, including product recalls, fines, and damage to the brand's reputation.
Conclusion
The Middle Eastern beauty market presents immense opportunities for brands willing to navigate its unique cultural and regulatory landscape. By respecting local traditions, obtaining necessary certifications, and ensuring compliance with regional regulations, brands can establish a successful and sustainable presence in this dynamic market. Whether through traditional retail channels or emerging digital platforms, the Middle East offers fertile ground for beauty brands to flourish and redefine the future of beauty.
As the industry continues to grow and evolve, brands that embrace innovation, cultural sensitivity, and regulatory compliance will find themselves well-positioned to capitalize on the region's burgeoning consumer base.