From Vanity Table to Kitchen: Beauty Brands Expanding Inside-Out
Introduction
The intersection of beauty and wellness has grown increasingly significant over the past few decades. Consumers are no longer satisfied with topical solutions alone; they increasingly seek “inner beauty” approaches - products that deliver visible results through nutritional support and holistic health benefits. Importantly, these ingestible formats are positioned as complementary rather than replacements - the promise being that consumers achieve the best results by combining topical care with supplements.
This evolution has catalyzed a wave of beauty brands extending their portfolios to include supplements, powders, capsules, and gummies designed to enhance skin, hair, and overall well-being from the inside out.
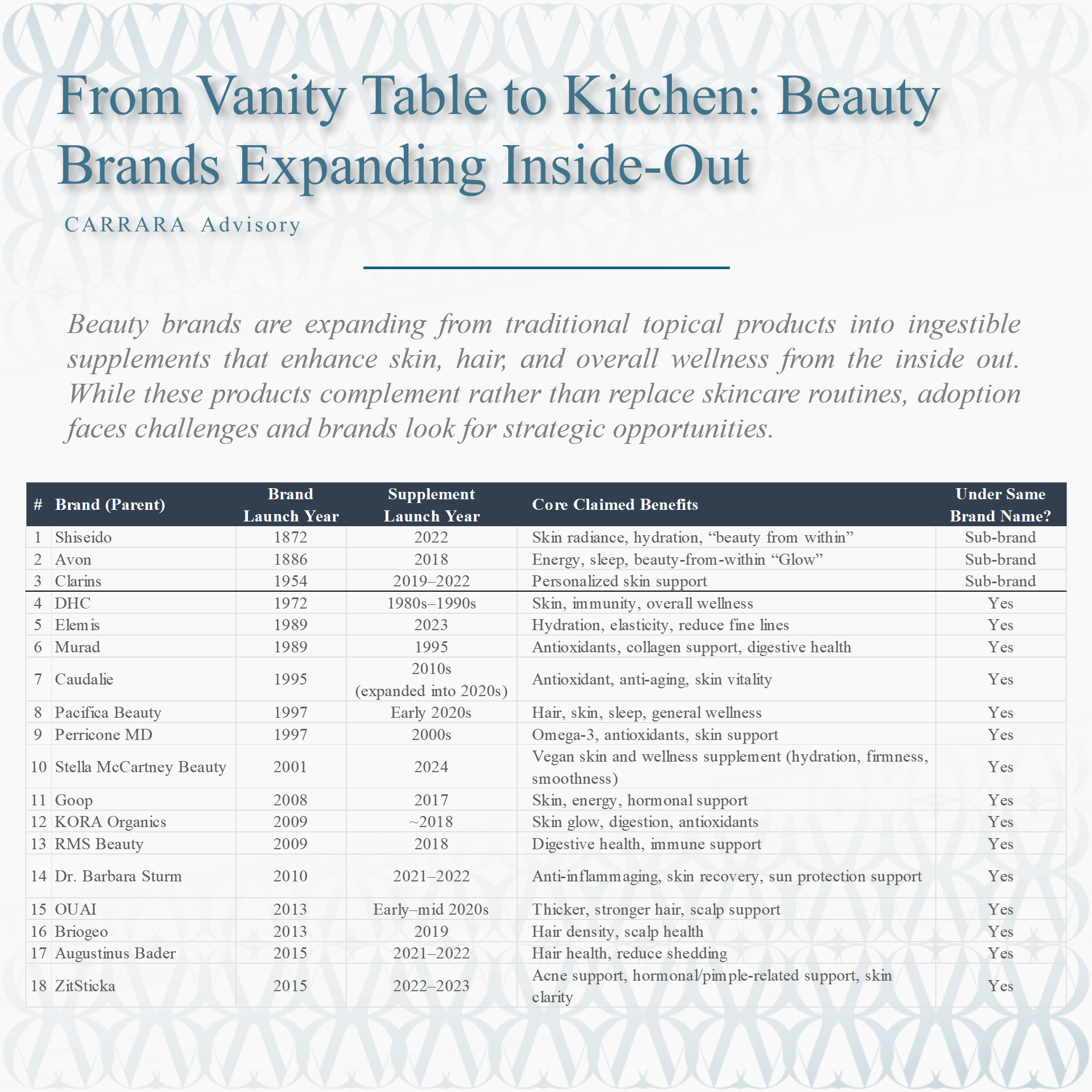
In this article we examine eighteen brands that have expanded from traditional beauty into supplements, tracing their historical origins, the timing and strategy of their supplement launches, product formats, and core claimed benefits. By analyzing these brands, we can uncover broader trends in the beauty and wellness market, understand the strategic motivations behind supplement lines, and explore consumer reception to this hybrid category.
Historical Context: Beauty Brands Before Supplements
The foundation of many modern beauty brands lies in the late 19th and 20th centuries, rooted in skincare, makeup, and fragrance. Some of these companies, such as Shiseido (1872) and Avon (1886), began as pioneers in cosmetic innovation, focusing exclusively on enhancing appearance through external application.
Shiseido, for example, built a legacy on scientific skincare, combining traditional Japanese philosophies with Western cosmetic research. Avon, with its direct-selling model, democratized access to beauty products, enabling widespread distribution of lotions, creams, and cosmetics. These brands had long established consumer trust and credibility, making them well-positioned to leverage their reputation when branching into the supplement sector.
Other brands, such as Clarins (1954) and DHC (1972), became known for plant-based, dermatologist-tested skincare and supplements supporting wellness. DHC, in particular, was an early adopter of ingestible health solutions, launching capsules for skin, immunity, and general wellness as early as the 1980s–1990s. These early moves illustrate the strategic foresight of some brands in recognizing the link between inner nutrition and outer beauty.
Motivations for Entering the Supplement Market
The decision to introduce supplements often stems from a combination of consumer demand, scientific validation, and brand positioning. There are several motivations behind these moves:
Consumer Demand for Holistic Solutions
Modern consumers increasingly associate beauty with overall wellness. Products that promise radiant skin, strong hair, or youthful vitality through internal support resonate with health-conscious demographics, especially millennials and Gen Z. For instance, brands like RMS Beauty and Goop tapped into this trend, offering as add-ons capsules to support digestive health, immunity, and hormonal balance alongside traditional skincare.
Brand Extension and Revenue Diversification
Supplements provide an opportunity for existing beauty brands to extend their product portfolios without diluting their core brand values. For example, Clarins launched myBlend, a personalized skin supplement range, while Shiseido introduced INRYŪ capsules targeting skin radiance. These sub-brands allow companies to experiment with wellness products while keeping the original beauty-focused brand intact.
Scientific Legitimacy and Credibility
Entering the supplement market allows brands to position themselves as scientifically informed wellness authorities. Perricone MD, for instance, expanded into skin and body supplements emphasizing omega-3s, antioxidants, and collagen support - leveraging its reputation as a dermatologist-led skincare brand to justify ingestible interventions. Similarly, Dr. Barbara Sturm’s STURM INSIDE promotes anti-inflammaging and skin recovery benefits, aligning with her established clinical skincare brand identity.
Competitive Differentiation
With the beauty market increasingly saturated, supplements provide differentiation and a premiumization opportunity. Brands such as Stella McCartney Beauty (Nourish by Stella) and Augustinus Bader (The Hair Revitalizing Complex) target high-end consumers, offering luxury wellness solutions that complement their premium beauty positioning.
Product Formats and Consumer Preferences
Examining the product formats of these topical-to-ingestible lines reveals a clear pattern: capsules dominate, followed by powders, gummies, and liquids.
Capsules: The most prevalent format, capsules offer convenience, precise dosing, and compatibility with a broad range of active ingredients. Shiseido’s INRYŪ, Murad’s Internal Skincare, Elemis Pro-Collagen Skin Future Supplements, and Stella McCartney Beauty’s Nourish all leverage capsules. Capsules convey a clinical, trustworthy image, appealing to consumers seeking measurable, reliable benefits.
Powders and Ampoules: Powder-based products, such as Clarins myBlend and KORA Organics Noni Glow Skinfood, emphasize personalization and freshness. Powders allow consumers to mix ingredients with beverages, often perceived as more natural or artisanal.
Gummies: Gummies represent a playful, approachable segment, appealing to younger demographics or consumers new to supplements. Pacifica Beauty’s Beauty Gummies and ZitSticka Supplements combine convenience with a positive sensory experience, offering benefits such as hair, skin, sleep support, and acne management.
Liquids: Liquids provide unique advantages over other formats. They allow for higher concentrations of active ingredients, supporting potentially faster or more potent effects. Single-dose or “one-shot” formats, including ampoules, enhance ease of use, reduce dosing errors, and improve adherence. When formulated with care, liquids and ampoules can also offer a pleasant taste, turning supplementation into a more enjoyable experience. Ampoules, in particular, reinforce premium or clinical positioning, emphasizing potency, freshness, and precision dosing.
The choice of format reflects not only consumer preferences but also marketing strategy and brand positioning. Capsules suggest clinical authority, powders suggest bespoke personalization, gummies suggest accessibility and fun, and liquids suggest potency, convenience, and a sensory, premium experience.
Core Claimed Benefits: From Beauty to Holistic Wellness
The shift from external beauty to internal wellness is evident in the claimed benefits of these products. They generally fall into three categories:
Skin-Focused Supplements
Many brands maintain a strong skincare orientation, translating their external expertise into internal formulations. Claims such as hydration, elasticity, reduction of fine lines, skin glow, and radiance are common. For instance:
Shiseido’s INRYŪ emphasizes skin radiance and hydration.
Elemis targets hydration, elasticity, and fine line reduction.
Caudalie’s Vinexpert Dietary Supplements focus on antioxidant protection and skin vitality.
Hair and Scalp Health
Hair health has become an increasingly important focus, especially in younger demographics and in markets like the U.S., U.K., and Japan. Supplements like OUAI’s Thick & Full Hair Capsules, Briogeo’s B.Well Supplements, and Augustinus Bader’s Hair Revitalizing Complex target hair density, scalp health, and reduced shedding.
General Wellness and Systemic Health
Some brands extend beyond beauty into broader wellness, addressing energy, sleep, digestion, immune support, and hormonal balance. Examples include:
Avon’s Espira line emphasizes energy, sleep, and overall glow.
Goop Wellness capsules provide skin, energy, and hormonal support.
RMS Beauty’s Within supplements support digestive health and immunity.
Murad’s Internal Skincare supports antioxidants, collagen, and digestive health.
Notably, brands increasingly adopt multi-benefit formulations, reflecting the consumer preference for “all-in-one” solutions. Pacifica Beauty’s gummies, which combine hair, skin, sleep, and general wellness benefits, illustrate this holistic approach.
Brand Strategy: Sub-Brands vs. Under Same Brand Name
Analyzing whether supplements are launched under the original brand or as a sub-brand provides insight into risk management and strategic positioning.
Sub-Brands: Shiseido’s INRYŪ, Avon’s Espira, and Clarins’ myBlend exemplify sub-brands. This approach allows experimentation with wellness without impacting the parent brand’s core positioning. Sub-brands can target different demographics or price points while maintaining parent brand equity.
Same Brand Name: DHC, Elemis, Murad, Caudalie, and others opted to launch supplements under the same brand name. This choice capitalizes on brand loyalty, leveraging established trust in skincare or beauty products to endorse ingestible solutions. Consumers familiar with Murad or Perricone MD are more likely to accept internal skincare supplements as credible extensions of existing expertise.
The choice between sub-branding and brand-extension depends on risk tolerance, consumer perception, and the degree of divergence between the original and new product categories. Sub-branding reduces reputational risk, while brand-extension maximizes leverage of existing credibility.
Chronological Analysis: Early Movers vs. Recent Entrants
The timeline of supplement launches reflects both market maturity and consumer trend adoption:
Early Movers (1980s–1990s): DHC (1980s–1990s) and Murad (1995) pioneered topical-to-ingestible. These early entrants were motivated by internal health trends and early recognition of nutraceuticals. Despite limited mainstream adoption at the time, they established credibility and proof of concept for ingestible beauty.
2000s Expansion: Brands like Perricone MD (2000s) and Goop (2017) expanded the concept, responding to increasing consumer awareness of nutrition and skin health. This period saw more evidence-based approaches, including antioxidant-rich formulations and collagen support.
2020s Surge: The early 2020s witnessed rapid growth in beauty supplement launches, reflecting wider wellness trends and the mainstreaming of nutraceuticals. Elemis (2023), Pacifica Beauty (early 2020s), OUAI (early–mid 2020s), and Stella McCartney Beauty (2024) demonstrate this wave. Notably, luxury brands such as Augustinus Bader and Stella McCartney target high-income consumers with premium formulations, signaling growing market segmentation within beauty-to-wellness supplements.
This timeline also mirrors broader trends in consumer health consciousness, social media influence, and digital marketing channels promoting wellness lifestyles.
Regional and Cultural Considerations
While the brands listed operate globally, their approach to supplement development often reflects regional differences:
Japan and Asia: Shiseido and DHC illustrate early adoption of beauty-from-within concepts, consistent with Japanese and Korean cultural norms emphasizing holistic health, skin perfection, and longevity. DHC’s early capsule formulations show alignment with local dietary supplement practices.
Europe: Brands like Clarins, Caudalie, and Augustinus Bader emphasize premium formulations, personalization, and luxury wellness narratives. European consumers value evidence-backed claims, natural ingredients, and holistic approaches integrating beauty and wellness.
North America: Goop, RMS Beauty, and OUAI reflect U.S. trends prioritizing functional benefits, lifestyle alignment, and celebrity or influencer endorsement. Gummies and accessible formats cater to younger audiences seeking convenient, multi-benefit solutions.
Global Trends: There is a convergence around capsules and powders for efficacy, alongside gummies for mass-market adoption. The claims emphasize antioxidant protection, collagen support, skin vitality, hair health, and systemic wellness, reflecting universal beauty concerns intertwined with broader wellness aspirations.
Marketing Strategies and Consumer Engagement
Successful beauty-to-wellness brands adopt integrated marketing strategies that leverage the credibility of the original brand, digital platforms, influencer partnerships, and lifestyle narratives:
Storytelling and Heritage
Brands like Shiseido and Clarins emphasize heritage, research, and science, creating narratives that reinforce credibility in wellness supplements. Murad and Perricone MD highlight clinical dermatology expertise to convey authority.
Digital and Social Media
Digital-first brands such as Goop, RMS Beauty, and Pacifica Beauty use social media to build communities around wellness, leveraging content, testimonials, and influencer endorsements to educate consumers on supplement benefits.
Personalization and Premiumization
Clarins’ myBlend and Augustinus Bader’s Hair Revitalizing Complex offer personalized approaches, aligning with consumers’ growing desire for bespoke wellness solutions. Premiumization is reinforced through high-quality ingredients, meticulous formulation, and elevated packaging.
Multi-Benefit Messaging
Modern consumers prefer efficiency and convenience. Pacifica Beauty and ZitSticka highlight multi-benefit formulations - hair, skin, sleep, immune, and digestive health - addressing multiple needs with a single product.
Challenges in Beauty-to-Wellness Expansion
While promising, the expansion into supplements poses several challenges:
Regulatory Compliance
Supplements are subject to complex regulatory frameworks varying by region. Brands must ensure safety, accurate labeling, and compliance with health claims. Missteps can damage credibility.
Consumer Education
Not all consumers readily accept beauty-from-within concepts. Effective education is required to convey safety, benefits, dosage, and expected outcomes. Brands must bridge the knowledge gap between topical skincare and internal supplementation.
Efficacy and Perception
Unlike topical products with immediate visual feedback, supplement benefits are gradual, potentially reducing perceived value. Brands must manage expectations and deliver scientifically backed formulations.
Market Saturation
As more beauty brands enter the supplement space, differentiation becomes challenging. Multi-benefit formulations, luxury positioning, and unique ingredients are key tools to stand out.
Sales Channel Ambiguity
In markets where ingestible beauty is less established, particularly in Europe, consumers are unsure where to buy these products - whether in beauty retailers, pharmacies, supermarkets, or supplement shops. This ambiguity reduces visibility and slows adoption, in contrast with Asia where the category already has a clear place in the retail landscape. For a deeper dive into this issue, see our dedicated article on supplements and nutricosmetic distribution.
The Brands in more Detail
1. Shiseido – INRYŪ (2022)
Brand Background: Founded in 1872, Shiseido is one of the world’s oldest and most prestigious skincare brands. Its reputation is built on research, innovation, and a blend of Japanese and Western beauty philosophies.
Supplement Launch Context: INRYŪ was launched in 2022 as a sub-brand, marking Shiseido’s re-launch into ingestible beauty. The product line focuses on capsules promoting skin radiance and hydration.
Strategic Insight: Shiseido leveraged decades of skincare expertise to ensure the supplement’s credibility. By positioning INRYŪ as a sub-brand, the company mitigates risk while exploring new revenue streams in the wellness category.
Market Reception: Initial consumer feedback praised INRYŪ for combining Shiseido’s skincare authority with scientific backing, though adoption is largely concentrated in Japan and East Asia, where beauty-from-within supplements are culturally familiar.
2. Avon – Espira by Avon (2018)
Brand Background: Established in 1886, Avon is known for its direct-selling model and accessible beauty products.
Supplement Launch Context: Espira, launched in 2018, includes powders and capsules targeting energy, sleep, and beauty-from-within benefits.
Strategic Insight: Avon leveraged its wide distribution network to reach mass-market consumers, emphasizing multi-benefit formulations to appeal to health-conscious shoppers.
Market Reception: Adoption has been moderate; while loyal Avon customers appreciated the brand extension, competing wellness-focused brands with a health-centric positioning pose challenges.
3. Clarins – myBlend (2019–2022)
Brand Background: Clarins, founded in 1954, is renowned for plant-based skincare and anti-aging solutions.
Supplement Launch Context: The myBlend range includes powders and ampoules tailored for personalized skin support. The staggered launch (2019–2022) reflects experimentation with personalization technology.
Strategic Insight: By emphasizing personalization, Clarins differentiates itself in a crowded supplement market. The approach aligns with consumer trends favoring bespoke nutrition and wellness.
Market Reception: Highly positive among premium consumers in Europe; the brand has successfully communicated a science-backed, luxury wellness image.
4. DHC – Various Supplements (1980s–1990s)
Brand Background: Established in 1972 in Japan, DHC combines cosmetics and dietary supplements.
Supplement Launch Context: Early adoption of capsules for skin, immunity, and general wellness, positioning DHC as a pioneer in ingestible beauty.
Strategic Insight: Early mover advantage allowed DHC to build credibility and trust. Its wide portfolio of supplements mirrors the Japanese emphasis on routine, preventative health.
Market Reception: Strong in Asia; DHC enjoys high consumer loyalty, and supplements are often purchased alongside skincare, reinforcing a “total beauty” ecosystem.
5. Elemis – Pro-Collagen Skin Future Supplements (2023)
Brand Background: Elemis, founded in 1989, is a luxury British skincare brand known for anti-aging formulations.
Supplement Launch Context: Launched in 2023, these capsules target hydration, elasticity, and fine line reduction.
Strategic Insight: By extending the Pro-Collagen line into supplements, Elemis capitalizes on existing brand equity and premium consumer trust.
Market Reception: Early reviews highlight the luxury positioning and perceived efficacy, particularly in the U.K. and U.S., with limited availability in Asia.
6. Murad – Internal Skincare (1995)
Brand Background: Founded in 1989, Murad is a dermatologist-led skincare brand emphasizing clinical solutions.
Supplement Launch Context: Internal Skincare capsules and powders support antioxidants, collagen, and digestive health.
Strategic Insight: Maintaining the same brand name reinforces clinical credibility. Supplements complement topical lines, presenting Murad as a holistic solution provider.
Market Reception: Highly positive among dermatology patients and wellness-focused consumers; the brand benefits from strong U.S. dermatology endorsements.
7. Caudalie – Vinexpert Dietary Supplements (2010s–2020s)
Brand Background: Caudalie, founded in 1995 in France, focuses on vinotherapy and antioxidant-rich skincare.
Supplement Launch Context: Vinexpert supplements target antioxidant support, anti-aging, and skin vitality.
Strategic Insight: By leveraging its vinotherapy heritage, Caudalie positions supplements as natural and scientifically supported.
Market Reception: Strong adoption in Europe, particularly in France and U.K., where consumers value natural anti-aging interventions.
8. Pacifica Beauty – Beauty Gummies (Early 2020s)
Brand Background: Established in 1997, Pacifica Beauty focuses on vegan, cruelty-free, and accessible products.
Supplement Launch Context: Gummies targeting hair, skin, sleep, and general wellness.
Strategic Insight: Gummies cater to younger demographics, aligning with the brand’s playful, approachable image.
Market Reception: Positive among Gen Z consumers; the format encourages habitual intake and enhances brand engagement.
9. Perricone MD – Skin & Total Body Supplements (2000s)
Brand Background: Launched in 1997 by dermatologist Nicholas Perricone, the brand is synonymous with anti-aging science.
Supplement Launch Context: Capsules and powders promoting omega-3s, antioxidants, and skin health.
Strategic Insight: Supplements reinforce the brand’s scientific credibility and clinical positioning.
Market Reception: Strong among U.S. wellness consumers; adoption has been slower in markets unfamiliar with dermatologist-led ingestible beauty.
10. Stella McCartney Beauty – Nourish by Stella (2024)
Brand Background: Stella McCartney Beauty combines fashion heritage with premium skincare.
Supplement Launch Context: Vegan capsules for hydration, firmness, and smoothness.
Strategic Insight: Supplements align with the brand’s ethical and luxury positioning. Launching under the main brand reinforces prestige and credibility.
Market Reception: Early adopters include eco-conscious, high-income consumers; the launch has generated significant media attention.
11. Goop – Goop Wellness (2017)
Brand Background: Founded by Gwyneth Paltrow in 2008, Goop is a lifestyle brand emphasizing wellness and functional beauty.
Supplement Launch Context: Capsules support skin, energy, and hormonal balance.
Strategic Insight: Supplements are a natural brand extension, emphasizing the founder’s philosophy of integrative wellness.
Market Reception: Polarizing; some consumers question efficacy, but strong community engagement and influencer marketing drive adoption.
12. KORA Organics – Noni Glow Skinfood (~2018)
Brand Background: Founded by Miranda Kerr in 2009, KORA Organics emphasizes certified organic, natural ingredients.
Supplement Launch Context: Powder promoting skin glow, digestion, and antioxidants.
Strategic Insight: Supplements align with the brand’s clean beauty ethos and emphasize holistic wellness.
Market Reception: Well-received among organic beauty enthusiasts; adoption in Asia limited due to lack of brand awareness.
13. RMS Beauty – “Within” Supplements (2018)
Brand Background: RMS Beauty, launched in 2009, emphasizes raw, organic ingredients and non-toxic beauty.
Supplement Launch Context: Capsules for digestive health and immune support.
Strategic Insight: Supplements reinforce the brand’s holistic philosophy and appeal to health-conscious consumers.
Market Reception: Popular in U.S. and U.K. clean beauty markets; less penetration in Asia.
14. Dr. Barbara Sturm – STURM INSIDE (2021–2022)
Brand Background: Launched in 2010, Dr. Barbara Sturm is known for clinical, anti-inflammaging skincare.
Supplement Launch Context: Capsules supporting anti-inflammaging, skin recovery, and sun protection.
Strategic Insight: Supplements extend the clinical, evidence-based positioning of the skincare line.
Market Reception: Positive among high-end European consumers seeking scientifically backed anti-aging solutions.
15. OUAI – Thick & Full Hair Supplements (Early–mid 2020s)
Brand Background: Founded in 2013, OUAI emphasizes haircare solutions for modern lifestyles.
Supplement Launch Context: Capsules supporting thicker, stronger hair and scalp health.
Strategic Insight: Supplements complement haircare products, offering a holistic approach to hair wellness.
Market Reception: Well-received in U.S. markets; the product appeals to millennial and Gen Z consumers with hair concerns.
16. Briogeo – B.Well Supplements (2019)
Brand Background: Briogeo, founded in 2013, emphasizes clean, natural haircare solutions.
Supplement Launch Context: Capsules targeting hair density and scalp health.
Strategic Insight: Supplements reinforce the brand’s “good-for-you” hair philosophy and offer an internal solution to complement topical products.
Market Reception: Positive among clean-beauty haircare consumers; popularity boosted by influencer campaigns.
17. Augustinus Bader – The Hair Revitalizing Complex (2021–2022)
Brand Background: Launched in 2015, Augustinus Bader is a premium skincare brand emphasizing regenerative science.
Supplement Launch Context: Capsules target hair health and reduce shedding.
Strategic Insight: Supplements leverage the brand’s scientific prestige and target high-end consumers.
Market Reception: Positive in luxury skincare circles; pricing positions it as aspirational.
18. ZitSticka – ZitSticka Supplements (2022–2023)
Brand Background: Founded in 2015, ZitSticka is known for acne-focused, science-backed skincare.
Supplement Launch Context: Gummies and capsules for acne, hormonal support, and skin clarity.
Strategic Insight: Supplements complement topical solutions, offering a holistic acne management system.
Market Reception: Popular among Gen Z consumers seeking convenient acne solutions; strong social media engagement drives awareness.
Comparative Insights Across Brands
Heritage vs. Modern Brands: Older brands (Shiseido, Avon, Murad) leverage heritage and trust, while newer entrants (OUAI, Pacifica, ZitSticka) use digital engagement and social media influence.
Sub-Brand vs. Same-Brand Strategy: Luxury and heritage brands tend to use sub-brands for experimental wellness launches; clinical brands often maintain the same brand name to leverage authority.
Format Innovation: Capsules dominate, powders offer personalization, and gummies target convenience and youth appeal.
Multi-Benefit Formulations: There is a clear trend toward multi-benefit solutions addressing skin, hair, and systemic wellness simultaneously.
Market Reception Trends: Early movers enjoy loyalty and credibility, while recent entrants rely on storytelling, influencer marketing, and digital-first engagement to build awareness.
Future Outlook
The beauty-to-wellness supplement market is poised for continued growth. Key trends shaping the future include:
Personalized Nutrition and Supplements: Custom formulations, DNA-based or lifestyle-tailored supplements, will cater to individual needs, offering higher perceived efficacy.
Integration with Digital Health: Apps and wearable devices may track wellness outcomes, integrating supplement intake with lifestyle monitoring.
Cross-Category Innovation: Blurring boundaries between beauty, wellness, and pharmaceuticals will likely continue, with multi-functional products combining topical and ingestible benefits.
Conclusion
The evolution from traditional beauty products to wellness-focused supplements reflects a profound shift in consumer expectations. Brands that once concentrated solely on external aesthetics now recognize the demand for holistic solutions promoting skin, hair, and overall wellness from within. Through capsules, powders, and gummies, these brands translate decades of skincare expertise into ingestible products, balancing clinical credibility, consumer appeal, and lifestyle alignment.
From early pioneers like DHC and Murad to recent entrants such as Elemis, Stella McCartney Beauty, and OUAI, the beauty-to-wellness trajectory demonstrates strategic foresight, marketing acumen, and responsiveness to evolving health-conscious trends. While challenges in regulatory compliance, consumer education, and market differentiation exist, the future of beauty supplements promises continued growth, innovation, and integration into the broader wellness landscape.
This evolution doesn’t mean abandoning traditional skincare - instead, it reinforces it. Ingestibles are marketed as synergistic companions, amplifying the effects of creams and serums rather than replacing them.
In essence, the beauty-to-wellness evolution is not merely a product expansion - it is a philosophical and strategic transformation, acknowledging that true beauty is cultivated both inside and out. As consumers increasingly embrace holistic health, the boundary between cosmetics and nutrition will blur, ushering in a new era of integrated beauty and wellness solutions.
#BeautyIndustry #Nutricosmetics #Wellness #HolisticBeauty #SkincareInnovation #BrandStrategy #LuxuryBeauty #ConsumerTrends #InsideOutBeauty #Supplements